Glossary of Color Theory Concepts and Terms
What is color?
Color wheel. Hue (center ring), muted colors (second ring), chromatic grays (third ring), achromatic grays (outer ring)
HUE: Purest form of a color (full saturation). Often the terms color and hue are used interchangeably, but color contains characteristics, hue being just one (value and saturation are the others). See related: Prismatic color
VALUE: Luminosity of a color. The amount of light or dark that a color reflects. It’s most easily expressed in a scale from white to black (with white being the highest value and black being the lowest value). See related: Tints, Tones, Shades
Value scale from white to black. Pure value is achromatic (meaning “without color”) and is made entirely by mixing different amounts of white and black.
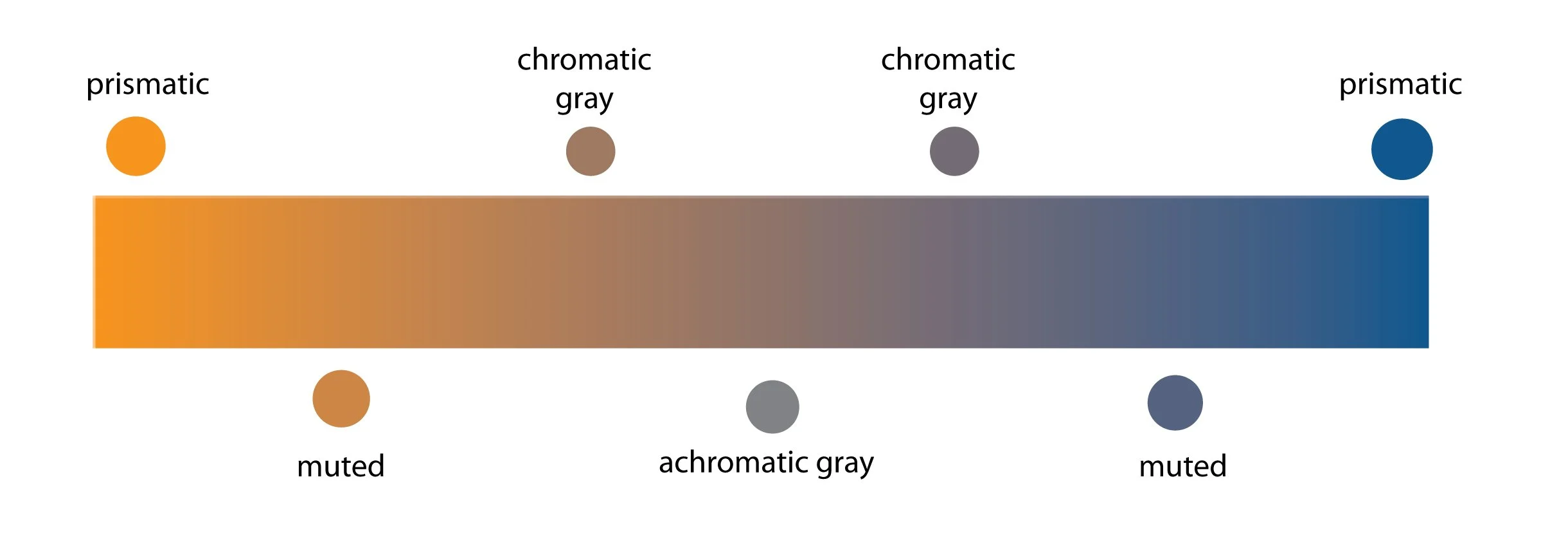
SATURATION: The purity of hue present in a color. Pure saturation is referred to as a prismatic color. To lower (or mute) a color’s saturation, you mix it with its complementary color. The saturation continuum has three levels:
Prismatic color (pure saturation)
Muted color (slightly duller version of a color that maintains its hue identity)
Chromatic grays (grays that have a perceptible hue identity)
Saturation continuum from prismatic color to muted color to chromatic grays.
PRISMATIC COLOR: The highest saturation level; As pure a hue as possible with pigments. See related: Saturation
MUTED COLOR: A saturation level that lie just outside the prismatic zone, created by adding black (shade), white (tint), gray (tone) or a complement of the hue. See related: Saturation, Prismatic Color, Tints, Tones, Shades
CHROMATIC GRAYS: A saturation level near the middle of the saturation continuum. Grays that exhibit a subtle, but discernible hue, created by adding larger amounts black (shade), white (tint), gray (tone) or a complement of a hue (muted color). See related: Saturation, Tints, Tones, Shades, Muted color
ACHROMATIC GRAYS: The saturation level at the very center of the saturation continuum. Grays that lack a perceptible hue and are derived from mixing black and white.
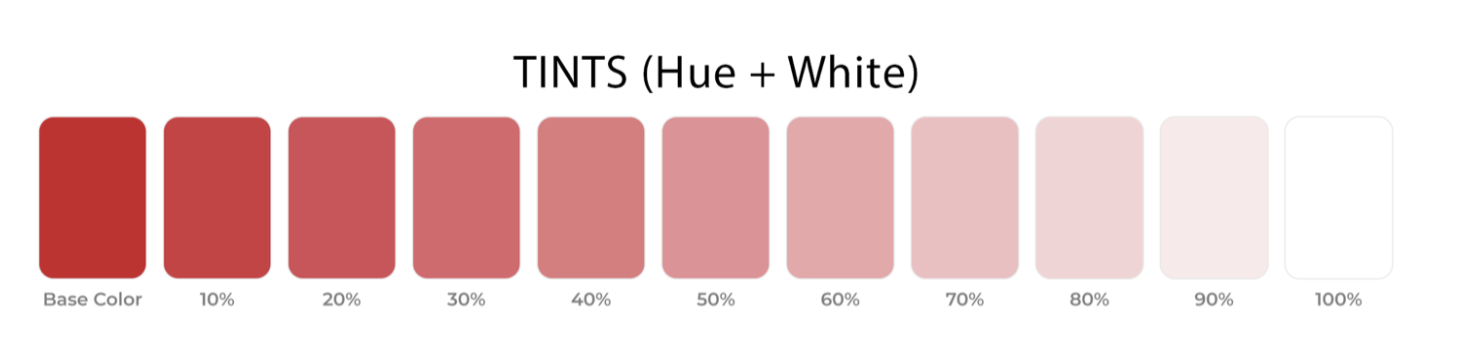
TINTS: A color mixed with white, which increases lightness. See related: Saturation
TONES: A color mixed with gray, or by both tinting and shading. Mixing a color with any neutral color (including black, gray, and white) reduces the chroma, or colorfulness, while the hue remains unchanged. See related: Saturation
SHADES: A color mixed with black, which increases darkness. See related: Saturation
COLOR SCHEME: An arrangement or combination of colors. See related: Color Harmony
COLOR HARMONY: A combination of colors that are aesthetically pleasing. There are several established models for harmonious color combinations, including: Complementary, Split Complementary, Triadic, and Analogous. See related: Color Scheme